
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)


ecological succession
Fire resets the stage for a healthy forest ecosystem
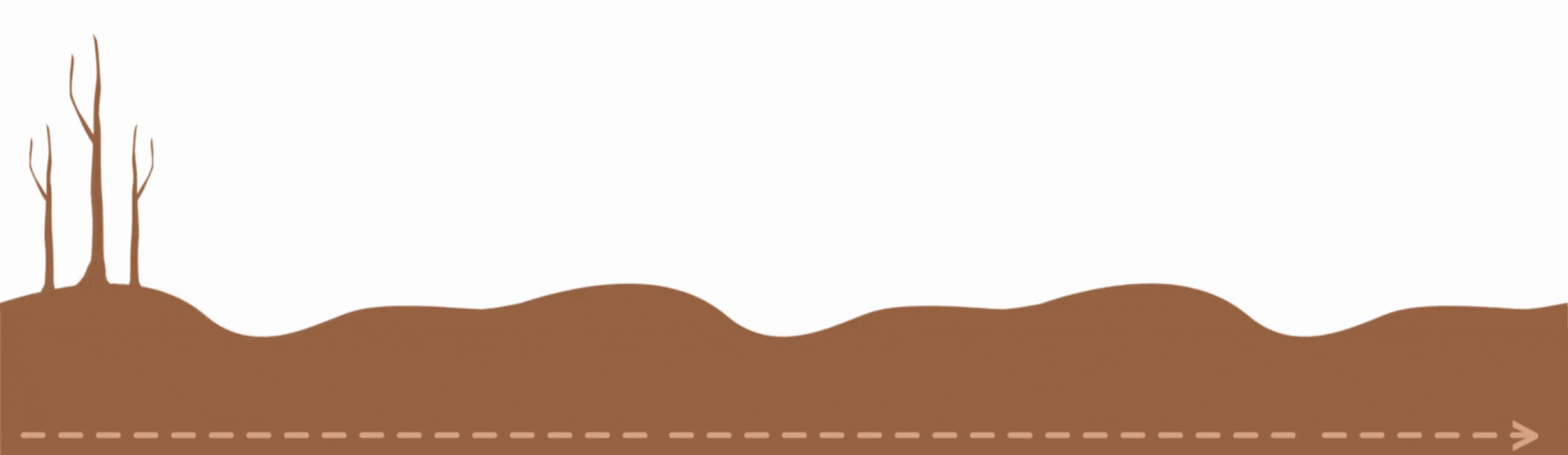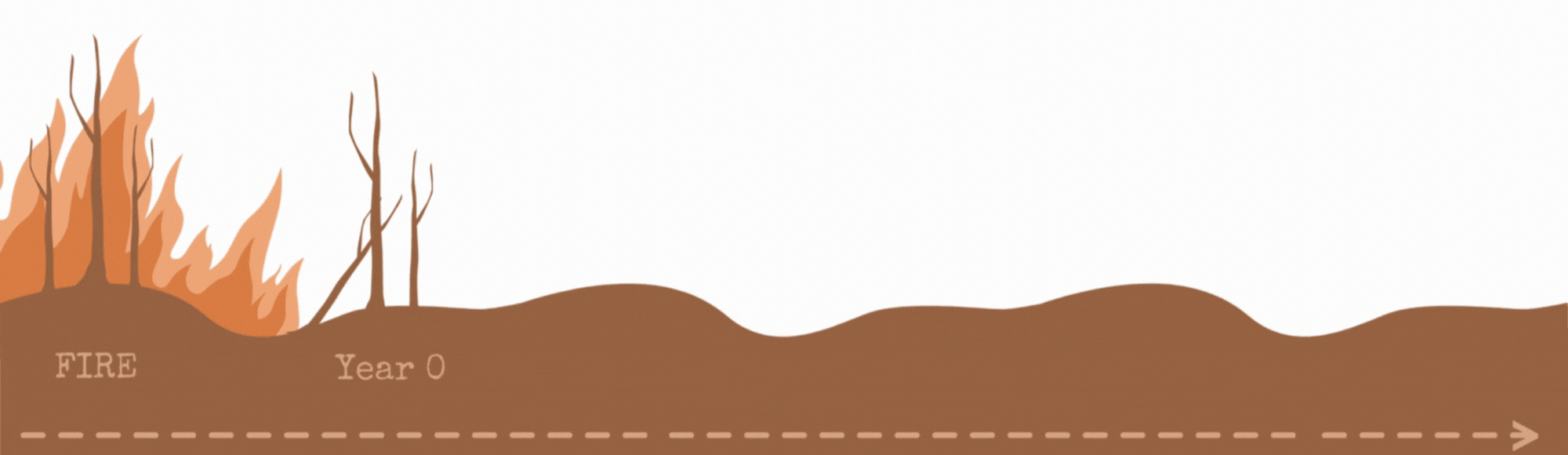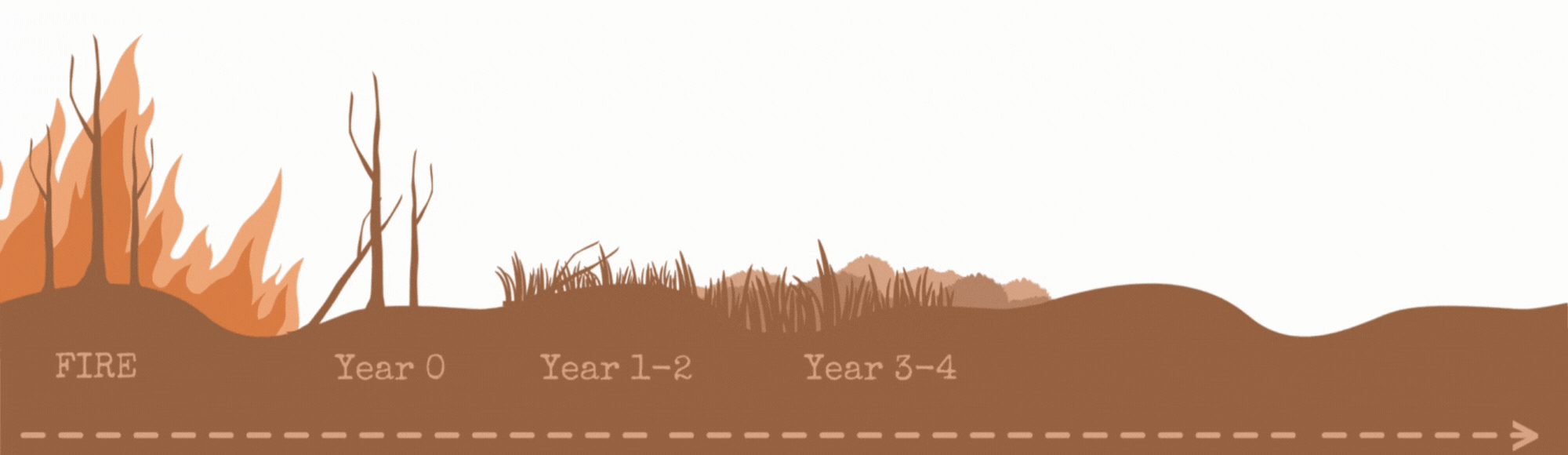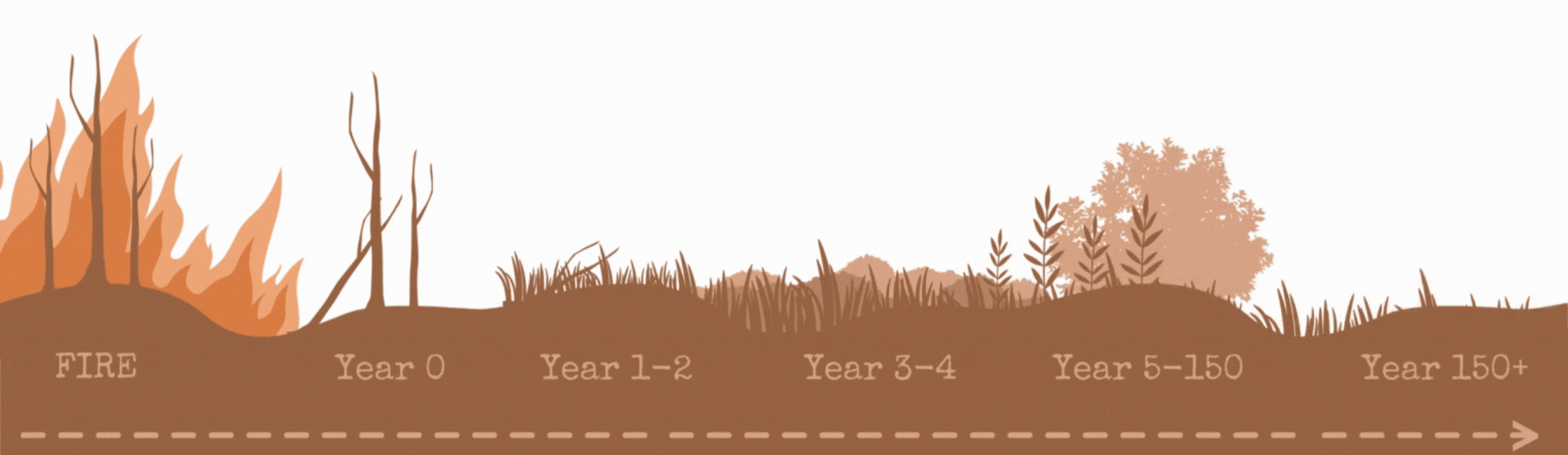
After a fire, plants and animals return to the affected area and repopulate. This process is called "ecological succession", referring to the change in the structure of a community over time. Some species repopulate more quickly, and others take much longer to regrow.
As you watch this forest replenish after a burn, what kinds of plants do you notice first? How do the colors and space change?
REBUILDING
Meet Katie Oliver.
Not only has she worked on some of the most notorious fires in recent Colorado memory, but she has also worked to rebuild the ecosystems and human structures in the wake of the damage. As you listen to this conversation about her experiences during and after the blaze, try to imagine the changes in the ecosystem she's describing. How does an overgrown forest differ from a forest that has just experienced a fire?


AFTER BURNS




You may think of mountains and forests of the Western United States when you picture a wildfire, but we'll discover how grasslands have evolved with more frequent burns.
Source: National Academy of Sciences
US Forest Service Data 1970-2000
Where to fires happen? What starts them? How do the animals and plants recover? US Parks Service Ranger Michael Matthes and Lyons, CO fire chief Rob Stumpf discuss the environmental impacts of wildfire.